PHOTOVOLTAIC PANELS
Renewable Energy from Alternative Sources
SOLAR PANELS
For a Better Future
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ON ENERGY SAVING
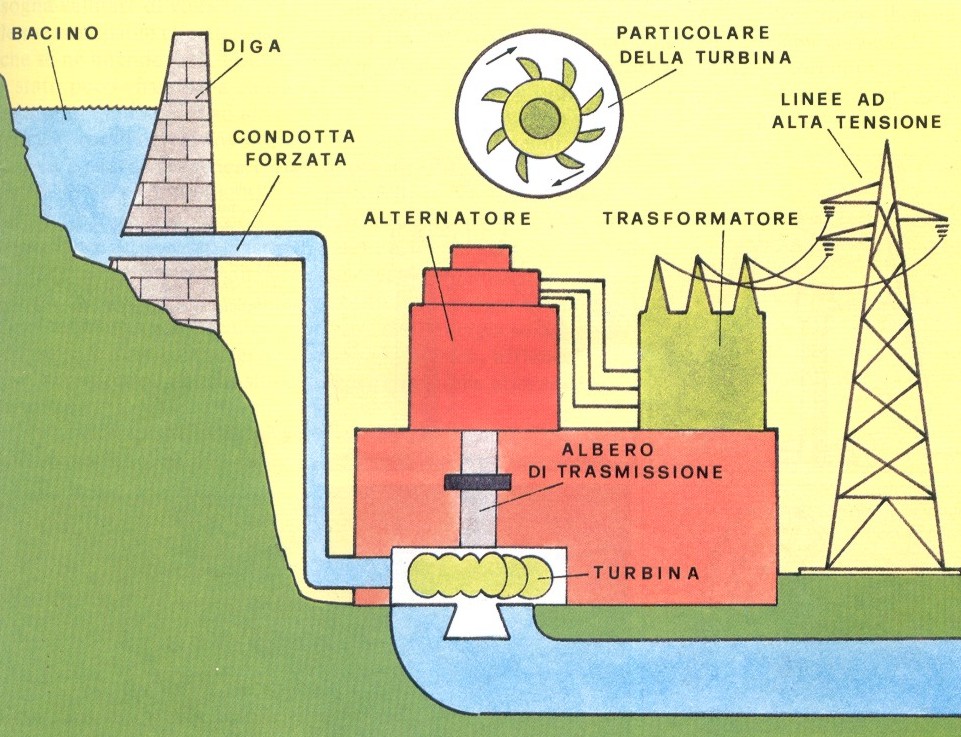
Hydropower Energy
Hydropower is the kind of energy that uses the gravitational potential energy transformation (owned by masses of water at the top) into kinetic energy to overcome a height difference, which kinetic energy is transformed, thanks to an alternator coupled to a turbine, into electricity.
Hydropower is derived from the course of rivers and lakes through the creation of dams and penstocks.
The power of a plant using a fall depends on two factors:
the door step of a mass of water through one point for a unit of time;
The leap height difference between the altitude where the water resource is flared and where it is returned to the natural environment through a turbine. The power of a system that uses a stream of water, however, depends on the speed of the current and the active surface of the turbine located. The plants can be:
For flowing water: hydroelectric plants located on the river,
A river basin, water is collected in a basin with a work of barrage or dam;
For storage: water is brought in to share means of pumps.
|
|
Plants in the basin (flow-adjusted)
They are the natural reservoir systems (lakes) or artificial, as in the case of many reservoirs, ponds are sometimes where you increase the capacity with barriers, in many cases the barriers consist of several tens of meters high dams.
Hydroelectric plants are now more powerful and more exploited, however, have a significant environmental impact, can be used as "accumulators" of energy use during peak hours pumping water from upstream to downstream during the night.
Plants or storage tank
systems are with all the features of traditional systems, but who derive the availability of water in the upper reservoir by means of electro-mechanical lifting (with pumps or turbines with the same production). This type of system consists of two ends of tanks, placed at different heights, connected by the artifacts of a typical hydroelectric plant: during daylight hours of greatest demand (peak hours) user stored water in the tank top is used to the production of electricity; in times of low demand (at night) the same is raised up to the upper reservoir. In this way the use of electricity to pump water into the upper reservoir is almost completely restored in a form more valuable because it returned in the hours of greatest demand.
|


